The Alps, overview & facts
- April 9, 2021
- 0
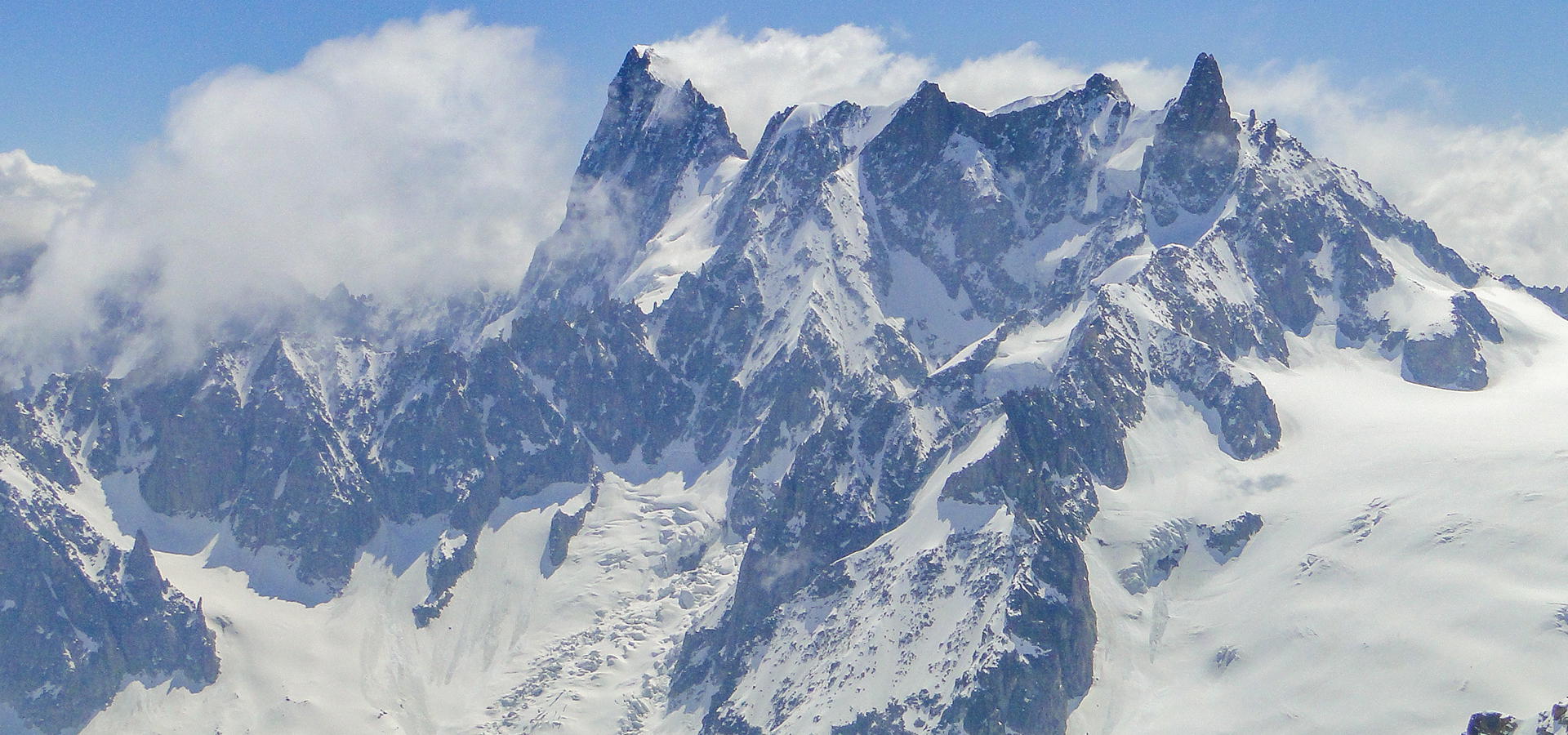
Cover image: Grandes Jorasses (Spyro Klitira)
The Alps are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lie in south-central Europe. The mountain range stretches approximately 1,200 kilometers in a crescent shape across eight Alpine countries: France, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, and Slovenia.
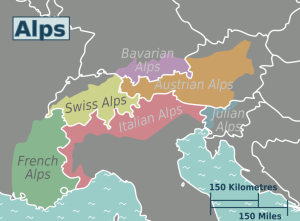
Highest peak:
Mont Blanc is the highest peak at 4,808 m. It is the second-highest and second most prominent mountain in Europe and the eleventh most prominent mountain summit in the world. The mountain stands between regions of Italy and of France. There are about a hundred peaks higher than 4,000 m in the Alpine region.

Rivers:
The Alps provide lowland Europe with drinking water, irrigation, and hydroelectric power. Although the area is only about 11% of the surface area of Europe, the Alps provide up to 90% of water to lowland Europe. Major European rivers flow from the Alps, including the Rhine, the Rhône, the Inn, and the Po.
Glaciers:
The major glacierized areas in the Alps are situated along the crest of the mountain chain, with the largest glaciers often found at the highest elevations. There are smaller glaciers scattered throughout the Alps.
The Swiss Alps is known for glaciers, containing around 1,800 glaciers. The region’s glaciers include the longest glacier in the Alps: the Aletsch Glacier.

Ecology:
The Alps are an interzonal mountain system (Orobiome), or a “transition area” between Central and Mediterranean Europe. The Alps have high habitat diversity, with 200 habitats classified throughout the mountain range. This mountain range is home to a high level of biodiversity.
According to the World Wildlife Foundation (WWF), there are over 4,500 species of plants, 200 bird species, 21 amphibian species, 15 reptile species, and 80 mammal species. Many of these species have made adaptations to the harsh cold conditions and high altitudes.
Additional Facts:
- At over 12 miles long and about a half-mile thick, the famous Aletsch valley glacier is the longest in the Alps, but due to climate change, the Aletsch is shrinking and predicted to completely melt by the end of this century.
- The Alps are Europe’s highest and most extensive mountain range.
- Mont Blanc is the highest mountain in the Alps, spanning 3 countries. Its granite ramparts distinguish it from other peaks. Mont Blanc’s ranges rose straight from the deep and are still rising, a phenomenon caused by glacial movement.
- The limestone Dolomites in Italy are half as high as Mont Blanc and were created as Africa’s collision with Europe pushed together an ancient tropical seafloor with the ancient skeletons of marine organisms into the sky.
- Humans have been living in the Alps since Paleolithic times, about 60,000 to 50,000 years ago. The Alpine region continues to have a strong cultural identity and its traditional culture of farming, cheesemaking, and woodworking still exists in Alpine villages. However, the tourism industry has been growing since the 20th century. While the region is home to 14 million people, it has 120 million annual visitors.
Source: https://www.pbs.org/











